 |
Lisp »Tips 'n Tricks
»Lisp & Lissajous
»1
»2
»3
»4
»5
»6
»7
LISAJU2 versione 2.0 genera figure di Lissajous bidimensionali da 3 formule, e in 3 output (punti, linee, coppie di archi).
Salvare LISP e DCL nella cartella pick/lisp oppure sostituire la stringa in rosso nel listato con un percorso a piacere.
LISAJU2.DCL
/*
LISAJU2.DCL (vers. 2.0)
Copyright (C) 2005 Claudio Piccini.
All rights reserved
www.cg-cad.com
*/
dcl_settings : default_dcl_settings { audit_level = 1; }
lisaju2 : dialog {
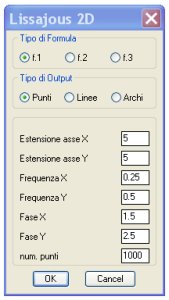
label = "Lissajous 2D";
: boxed_radio_row {
label = "Tipo di Formula";
: radio_button {
label = "f.1";
key = "f1";
value= "1";
}
: radio_button {
label = "f.2";
key = "f2";
}
: radio_button {
label = "f.3";
key = "f3";
}
}
: boxed_radio_row {
label = "Tipo di Output";
: radio_button {
label = "Punti";
key = "o1";
value= "1";
}
: radio_button {
label = "Linee";
key = "o2";
}
: radio_button {
label = "Archi";
key = "o3";
}
}
: row {
: column {
: boxed_column {
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "Estensione asse X";
key = "xL";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "Estensione asse Y";
key = "yH";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "Frequenza X";
key = "xF";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "Frequenza Y";
key = "yF";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "Fase X";
key = "xPh";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "Fase Y";
key = "yPh";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
: row {
: edit_box {
label = "num. punti";
key = "steps";
edit_width = 4;
}
}
}
}
}
: row {
: spacer {
width = 1;
}
: button {
label = "OK";
is_default = true;
key = "accept";
width = 8;
fixed_width = true;
}
: button {
label = "Cancel";
is_cancel = true;
key = "cancel";
width = 8;
fixed_width = true;
}
: spacer {
width = 1;
}
}
}
//eof
|
LISAJU2.LSP
;|
LISAJU2.LSP (vers. 2.0)
Copyright (C) 2005 Claudio Piccini.
All rights reserved
www.cg-cad.com
Generatore di figure di Lissajous bidimensionali
Formula 1:
x = xL*sin(xF*e+xPh)
y = yH*sin(yF*e+yPh)
Formula 2:
x = xL*sin(xF*e+xPh)
y = yH*sin(e)
Formula 3:
x = x+(xL*sin(xF*e+xPh))
y = y+(yH*sin(e))
Output: punti, linee, coppie di archi.
Il metodo dei 2 archi e' basato su:
C.A. Pickover, "La matematica di Oz"
(n.84 "L'overdrive della strega")
Franco Muzzio Editore (2004)
|;
(defun myerror (s)
(if (/= s "Function cancelled")
(princ (strcat "\nError: " s))
)
(ripVar)
(princ)
)
(defun salVar ()
(setq orto (getvar "orthomode"))
(setq snapp (getvar "osmode"))
(setq snm (getvar "snapmode"))
(setq piano (getvar "clayer"))
)
(defun ripVar ()
(command "_redraw")
(setvar "cmdecho" 1)
(setvar "osmode" snapp)
(setvar "snapmode" snm)
(setvar "orthomode" orto)
(setvar "clayer" piano)
(setq *error* olderr)
(princ)
)
(defun ripGlo ()
(setq #05ls1 xL) ; parametro reale xL (est. asse X)
(setq #05ls2 yH) ; parametro reale yH (est. asse Y)
(setq #05ls3 xF) ; parametro reale xF (frequenza X)
(setq #05ls4 yF) ; parametro reale yF (frequenza Y)
(setq #05ls5 xPh) ; parametro reale xPh (fase X)
(setq #05ls6 yPh) ; parametro reale yPh (fase Y)
(setq #05ls7 steps) ; parametro intero steps (numero punti)
)
(defun defaults ()
(setq xL #05ls1)
(setq yH #05ls2)
(setq xF #05ls3)
(setq yF #05ls4)
(setq xPh #05ls5)
(setq yPh #05ls6)
(setq steps #05ls7)
(set_tile "xL" (rtos 0.00 2))
(set_tile "yH" (rtos 0.00 2))
(set_tile "xF" (rtos 0.00 2))
(set_tile "yF" (rtos 0.00 2))
(set_tile "xPh" (rtos 0.00 2))
(set_tile "yPh" (rtos 0.00 2))
(set_tile "steps" (rtos 0 2))
(setq #05ls1 (rtos #05ls1 2 2))
(setq #05ls2 (rtos #05ls2 2 2))
(setq #05ls3 (rtos #05ls3 2 2))
(setq #05ls4 (rtos #05ls4 2 2))
(setq #05ls5 (rtos #05ls5 2 2))
(setq #05ls6 (rtos #05ls6 2 2))
(setq #05ls7 (rtos #05ls7 2 0))
(set_tile "xL" #05ls1)
(set_tile "yH" #05ls2)
(set_tile "xF" #05ls3)
(set_tile "yF" #05ls4)
(set_tile "xPh" #05ls5)
(set_tile "yPh" #05ls6)
(set_tile "steps" #05ls7)
(setq formula 1) ; tipo di formula
(cond
((= formula 1)(set_tile "f1" "1"))
((= formula 2)(set_tile "f2" "1"))
((= formula 3)(set_tile "f3" "1"))
)
(setq outp 1) ; tipo di output (punti,linee,archi)
(cond
((= outp 1)(set_tile "o1" "1")) ; punti
((= outp 2)(set_tile "o2" "1")) ; linee
((= outp 3)(set_tile "o3" "1")) ; archi
)
)
(defun do_xL ()
(setq xL (atof (get_tile "xL")))
)
(defun do_yH ()
(setq yH (atof (get_tile "yH")))
)
(defun do_xF ()
(setq xF (atof (get_tile "xF")))
)
(defun do_yF ()
(setq yF (atof (get_tile "yF")))
)
(defun do_xPh ()
(setq xPh (atof (get_tile "xPh")))
)
(defun do_yPh ()
(setq yPh (atof (get_tile "yPh")))
)
(defun do_Steps ()
(setq steps (atoi (get_tile "steps")))
)
(defun lissajous2 ( x y i / e xx yy
p1 p2 p3 p4
)
(if (< i steps)
(progn
(cond
((= formula 1)
(setq e (* 1.0 i))
(setq xx (* xL (sin (+ (* xF e) xPh))))
(setq yy (* yH (sin (+ (* yF e) yPh))))
)
((= formula 2)
(setq e (+ (* 1.0 i)(/ 1.0 steps)))
(setq xx (* xL (sin (+ (* xF e) xPh))))
(setq yy (* yH (sin e)))
)
((= formula 3)
(setq e (+ (* 1.0 i)(/ 1.0 steps)))
(setq xx (+ x (* xL (sin (+ (* xF e) xPh)))))
(setq yy (+ y (* yH (sin e))))
)
)
(cond
((= outp 1) ; punto
(command "_point" (list (+ xx (car pStart))(+ yy (cadr pStart))))
)
((= outp 2) ; linea
(if (> i 0)
(command "_line"
(list (+ x (car pStart))(+ y (cadr pStart)))
(list (+ xx (car pStart))(+ yy (cadr pStart)))
""
)
(command "_point" (list (+ xx (car pStart))(+ yy (cadr pStart))))
)
(setq x xx)
(setq y yy)
)
((= outp 3) ; coppia di archi
(if (> i 0)
(progn
(setq p1 (list (+ x (car pStart))(+ y (cadr pStart))))
(setq p2 (list (+ xx (car pStart))(+ yy (cadr pStart))))
(setq p3 (polar p1 (+ (angle p1 p2) 0.523599) 0.1))
(setq p4 (polar p1 (- (angle p1 p2) 0.523599) 0.1))
(command "_arc" p1 "_e" p2 "_d" p3) ; +30 gr.
(command "_arc" p1 "_e" p2 "_d" p4) ; -30 gr.
)
(command "_point" (list (+ xx (car pStart))(+ yy (cadr pStart))))
)
(setq x xx)
(setq y yy)
)
)
(lissajous2 x y (+ i 1))
)
)
)
(defun c:lisaju2 (/ olderr snapp snm orto piano
dcl_id ok_c
outp steps
xL yH xF yF xPh yPh
pStart
)
(setq olderr *error* *error* myerror)
(setvar "cmdecho" 0)
(salVar)
(command "_osnap" "_non")
;
; Variabili globali:
; #05ls1 #05ls2 #05ls3
; #05ls4 #05ls5 #05ls6 #05ls7
;
(if (= #05ls1 nil)(setq #05ls1 5.0)) ; xL
(if (= #05ls2 nil)(setq #05ls2 5.0)) ; yH
(if (= #05ls3 nil)(setq #05ls3 0.25)) ; xF
(if (= #05ls4 nil)(setq #05ls4 0.5)) ; yF
(if (= #05ls5 nil)(setq #05ls5 1.5)) ; xPh
(if (= #05ls6 nil)(setq #05ls6 2.5)) ; yPh
(if (= #05ls7 nil)(setq #05ls7 1000)) ; numero di punti
(setq ok_c 1)
(if (< (setq dcl_id (load_dialog "c:/pick/lisp/lisaju2.dcl")) 0)(exit))
(if (not (new_dialog "lisaju2" dcl_id))(exit))
(defaults)
(action_tile "f1" "(setq formula 1)")
(action_tile "f2" "(setq formula 2)")
(action_tile "f3" "(setq formula 3)")
(action_tile "o1" "(setq outp 1)") ; punti
(action_tile "o2" "(setq outp 2)") ; linee
(action_tile "o3" "(setq outp 3)") ; archi
(action_tile "xL" "(do_xL)")
(action_tile "yH" "(do_yH)")
(action_tile "xF" "(do_xF)")
(action_tile "yF" "(do_yF)")
(action_tile "xPh" "(do_xPh)")
(action_tile "yPh" "(do_yPh)")
(action_tile "steps" "(do_Steps)")
(action_tile "accept" "(done_dialog)")
(action_tile "cancel" "(setq ok_c 0)")
(start_dialog)
(unload_dialog dcl_id)
(if (= 1 ok_c)
(progn
(ripGlo)
(setq pStart (getpoint "\n seleziona un punto nel disegno..."))
(lissajous2 0 0 0)
(ripVar)
)
(progn
; valori globali di default
(setq #05ls1 5.0) ; xL
(setq #05ls2 5.0) ; yH
(setq #05ls3 0.25) ; xF
(setq #05ls4 0.5) ; yF
(setq #05ls5 1.5) ; xPh
(setq #05ls6 2.5) ; yPh
(setq #05ls7 1000) ; numero di punti
(ripVar)
)
)
)
;;;eof
|
Analisi del Lisp
In AutoCAD esiste più di un metodo per disegnare un arco, LISAJU2 (versione 2.0) usa il metodo Punto_Inizio, Punto_Fine, Direzione:
(setq p1 (list (+ x (car pStart))(+ y (cadr pStart))))
(setq p2 (list (+ xx (car pStart))(+ yy (cadr pStart))))
(setq p3 (polar p1 (+ (angle p1 p2) 0.523599) 0.1))
(setq p4 (polar p1 (- (angle p1 p2) 0.523599) 0.1))
(command "_arc" p1 "_e" p2 "_d" p3) ; +30 gr.
(command "_arc" p1 "_e" p2 "_d" p4) ; -30 gr.
Per ogni step il lisp disegna una coppia di archi opposti, con il metodo Inizio, Fine, Direzione. La direzione viene data da 2 punti.
I 2 punti (p3 p4 nel listato) si ottengono con la funzione (polar pt ang dist), con ang=30° e dist=0.1.
Test del Lisp
Tipo formula: 1 | Tipo Output: Archi | 5, 5, 2.5, 2.5, 3, -1.5, 500

Tipo formula: 1 | Tipo Output: Archi | 5, 5, 0.25, 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 100
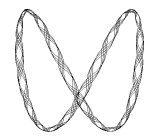
Tipo formula: 3 | Tipo Output: Archi | 5, 5, 0.25, 1.5, 3, 3, 500
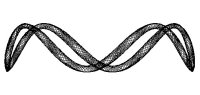
Tipo formula: 1 | Tipo Output: Archi | 5, 5, 0.7, 0.7, 8.01, 2.55, 200

Fonti bibliografiche:
C.A. Pickover. La matematica di Oz, (enigma n.84 "L'overdrive della strega"). Franco Muzzio Editore (2004)
Lisp »Tips 'n Tricks
Ultimo Aggiornamento_Last Update: 13 Maggio 2005
|
 |






