 |
Lisp »Tips 'n Tricks
»Lisp & 3dmesh
Una mesh 3d viene costruita definendo il numero di vertici rispetto alla direzione M e alla direzione N e inserendo le coordinate x y z di ciascun vertice.
Esempio:
3dmesh
Dim M della mesh : 2
Dim N della mesh : 2
Vertice (0,0) : 10,10,-1
Vertice (0,1) : 10,20,1
Vertice (1,0) : 20,10,1
Vertice (1,1) : 20,20,0
Il processo per generare una mesh è quindi molto lungo e di conseguenza è facile l'errore; questo è uno di quei casi dove l'implementazione in AutoLISP di un comando CAD è necessario e non superfluo.
Come esempio d'uso del comando 3dmesh ecco f3dm un lisp che traduce uno script di Python per generare funzioni 3D *
f3dm
;|
f3dm Copyright (C) 2005 by Claudio Piccini.
All rights reserved
www.cg-cad.com
Generatore di funzioni 3D
Traduce Function_plotter.py (C) by C. Wartmann
Oktober 1999
|;
(defun pow2 ( a )(setq a (* a a)))
(defun c:f3dm ( / snapp
M N
xw yw
x y z r
distZ distZZ
)
(setvar "cmdecho" 0)
(setq snapp (getvar "osmode"))
(command "_osnap" "_non")
(setq xw 0.5 yw 0.5)
; dim M mesh
(while
(progn
(initget (+ 2 4)) ; M>0
(setq M (getint "\n Dim M della mesh [2..256] <50>: "))
(if (= M nil)(progn (setq M 50) nil) T)
(if (and (>= M 2)(<= M 256)) nil T)
)
)
; dim N mesh
(while
(progn
(initget (+ 2 4)) ; N>0
(setq N (getint "\n Dim N della mesh [2..256] <50>: "))
(if (= N nil)(progn (setq N 50) nil) T)
(if (and (>= N 2)(<= N 256)) nil T)
)
)
(initget (+ 2 4)) ; distZ>0
(setq distZ (getreal "\n Disturbo asse Z <10>: "))
(if (= distZ nil)(setq distZ 10))
(setq distZZ (/ distZ 2))
(command "3dmesh" M N)
(setq y 0)
(while (< y M)
(setq x 0)
(while (< x N)
(setq r (sqrt (+ (pow2 (- x (/ N 2)))(pow2 (- y (/ M 2))))))
(setq z (* (sin (* r xw))(cos (* r yw))(exp (/ (* -1 r) distZZ)) distZ))
(command (list x y z))
(setq x (1+ x))
)
(setq y (1+ y))
)
(setvar "osmode" snapp)
(command "_redraw")
(setvar "cmdecho" 1)
(princ)
)
;;;eof
|
Test del Lisp
Command: f3dm
Dim M della mesh [2..256] <50>: Invio
Dim N della mesh [2..256] <50>: Invio
Disturbo asse Z <10>: Invio
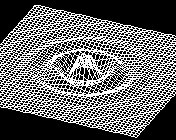
Command: f3dm
Dim M della mesh [2..256] <50>: Invio
Dim N della mesh [2..256] <50>: Invio
Disturbo asse Z <10>: 15
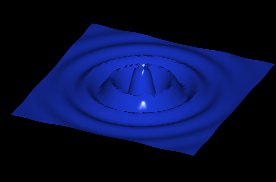
(*) C. Wartmann, Blender, la guida - 2001, Mondadori
# Function_plotter.py, Oktober 1999
# C. Wartmann@bigfoot.de
import Blender
from Blender import NMesh,Object
from Blender.NMesh import Col
from math import sin,cos,sqrt,exp
xw=0.5
yw=0.5
xmax=36 # x resolution
ymax=36 # y resolution
me2=NMesh.GetRaw()
# crea i vertici
for y in range(0,ymax):
for x in range(0,xmax):
r=sqrt((x-xmax/2)**2+(y-ymax/2)**2)
z=sin(r*xw)*cos(r*yw)*exp(-r/5)*10
v=NMesh.Vert(x,y,z)
me2.verts.append(v)
# collega i vertici alle facce
for y in range(0,ymax-1):
for x in range(0,xmax-1):
a=x+y*ymax
f=NMesh.Face()
f.v.append(me2.verts[a])
f.v.append(me2.verts[a+ymax])
f.v.append(me2.verts[a+ymax+1])
f.v.append(me2.verts[a+1])
me2.faces.append(f)
NMesh.PutRaw(me2,"Function",1)
Blender.Redraw()
|
Lisp »Tips 'n Tricks
Ultimo Aggiornamento_Last Update: 5 Agosto 2005
|
 |



